Published on
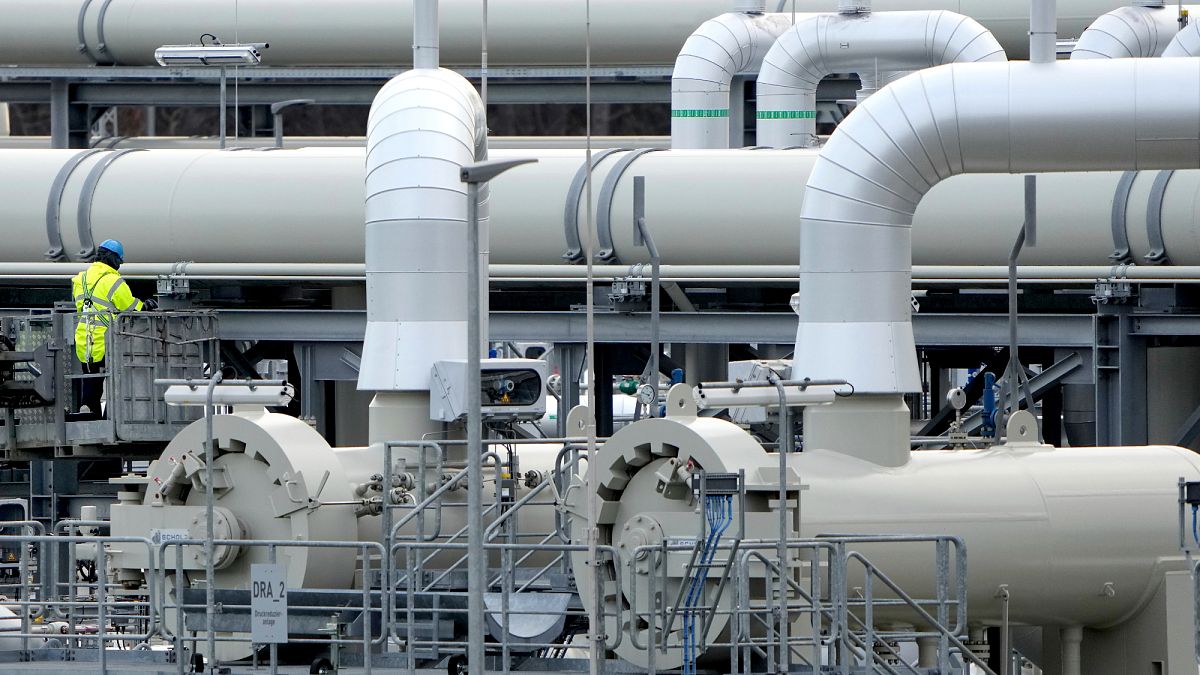
The European Commission published a new legislative proposal on Tuesday on how the bloc must phase out Russian oil and gas by 2027.
The proposal outlines the deadlines and strategies for EU countries to progressively reduce, and ultimately end, their reliance on Russia as a fuel supplier, as part of the REpowerEU Plan.
The proposal does not address nuclear energy, with a senior European Commission official telling journalists that that would be addressed separately.
Since the beginning of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, the EU has progressively reduced the trade of oil, gas and nuclear material from Russia.
As of 2024, the EU still relied on Russian imports for 19% of its gas and 3% of its crude oil supply.
“Russia has repeatedly attempted to blackmail us by weaponising its energy supplies. We have taken clear steps to turn off the tap and end the era of Russian fossil fuels in Europe for good,” European Commission president Ursula von der Leyen said.
The proposal
Under the draft rules, new contracts for Russian gas will be banned starting 1 January 2026. Existing short-term contracts must end by 17 June 2026, with limited exceptions for landlocked countries tied to long-term agreements, which will be allowed until the end of 2027.
Long-term contracts for Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) terminal services involving Russian companies will also be prohibited, freeing up infrastructure for alternative suppliers.
EU countries will be required to submit detailed diversification plans outlining specific steps and milestones to replace Russian energy imports.
Criticism from Hungary and Slovakia
In a meeting between EU ministers for energy on Monday, Hungary and Slovakia expressed their disagreements with the plan.
“Energy policy is a national competence and this endangers our sovereignty and energy security. Given the Middle East escalation, we proposed no such plan be tabled at all,” Hungary’s Foreign Minister Péter Szijjártó wrote in a post on X.
Despite this opposition, the European Commission decided to move forward with the text.
The Danish government, which will take over the presidency of the Council of the EU on 1 July, wants to reach a political agreement on the text as soon as possible.
Lars Aagaard, Danish Minister for Climate and Energy, told journalists on Monday that the Danish presidency will make an effort to “reach [political approval] as fast as possible,” adding: “If we succeed in concluding [the legislation] before New Year, I think that we have done a tremendous job.”
Next steps
The legislation will follow the standard procedure. The co-legislators, namely the European Parliament and the Council of the EU, will negotiate their own position on the file.
Afterwards, the text will enter inter-institutional negotiations, the so-called trilogue, to find a political agreement.
EU member states in the Council will need a qualified majority to approve the proposal on their side.
This reinforced majority requires the support of at least 15 of the 27 member states, representing at least 65% of the EU population.
The European Parliament will vote on the proposal by a simple majority vote.
Read the full article here