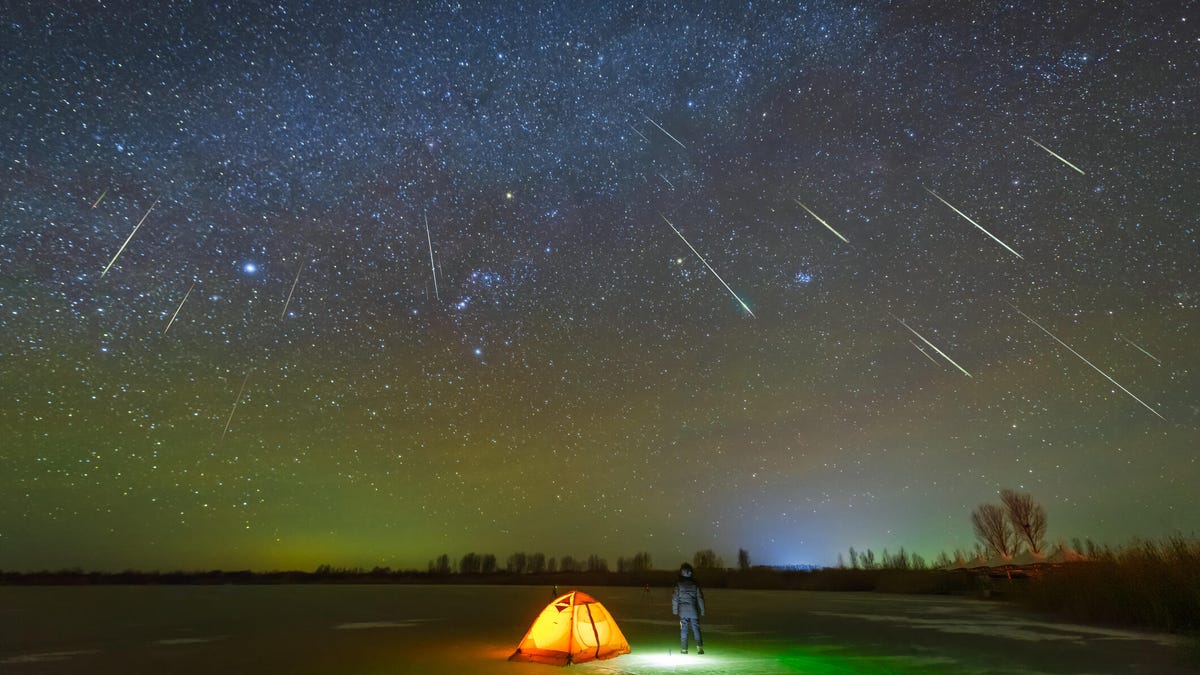
While meteor showers happen all year, a rarer occurrence is having two meteor showers that peak at the same time. It’ll happen this week, on Tuesday.
The shooting star show comes courtesy of the Alpha Capricornids and Southern delta Aquariids meteor showers. The former is already happening and runs until Aug. 12, with a peak on Tuesday. Southern delta Aquariids will start on Monday, peaks early on Tuesday and runs until Aug. 12 as well. That means for one evening, the two meteor showers are peaking at the same time, giving stargazers a much better chance at catching a shooting star.
Of the two, the Southern delta Aquarids is typically the larger meteor shower, tossing upward of 25 meteors per hour during its zenith. Alpha Capricornids is a lesser meteor shower, with about five per hour on average. Combined, they’ll output an estimated 30 per hour.
See 2 meteor showers at once
Since the meteors are coming from two different points in the sky, you would think spotting meteors from both would be difficult, but that is far from the truth.
Alpha Capricornids, which hails from the 169P/NEAT comet, originates from the Capricornus constellation. It will rise from the eastern skies across the continental US around sunset and streak across the southern sky, setting in the western sky at sunrise.
For the Southern delta Aquariids, its radiant — the point from which its meteors seem to originate — is the Aquarius constellation. Aquarius is right next to Capricornus. That means it also rises out of the eastern horizon, streaks across the southern sky, and sets in the western horizon around dawn.
If you have trouble finding either of them, Stellarium’s free sky map will help you hunt them down. Set the time, date and location, and you’re off to the races. Once you find one, the other one is essentially right there next to it.
Tips on watching meteor showers
As per the norm, the tips here are the same as they are for the aurora borealis and planet parades. Light pollution and weather are your two biggest enemies. Since you can only do anything about one of those, let’s focus on light pollution. You’ll want to drive as far away from the city and suburbs as possible, as the light pollution will make it difficult to see the dimmer meteors. The farther away you are, the better, as even suburban light pollution can obfuscate most meteors.
Once out there, you just have to sit and wait. Since the constellations will move across the south as you watch, you may have to rotate your chair if you’re out there for a while. Otherwise, a pair of binoculars may help. Telescopes aren’t recommended, as they obscure your field of view and may actively obstruct your ability to see meteors.
Read the full article here